Greater Mexico City

Greater Mexico City refers to the conurbation around Mexico City, officially called Mexico City Metropolitan Area (Zona Metropolitana de la Ciudad de México),[1] constituted by the Federal District—itself composed of 16 boroughs—and 41 adjacent municipalities of the states of Mexico and Hidalgo. For normative purposes, however, Greater Mexico City most commonly refers to the Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico (Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México) an agglomeration that incorporates 18 additional municipalities. As of 2009, Greater Mexico City has population of 21,163,226, making it the third largest metropolitan area in the world and the most populous metropolitan area in the Americas.[2]
Since the 1940s there have been different proposals to establish the limits of the growing conurbation of Mexico City, and different definitions were used unofficially as the city continued to grow. The Federal Government (represented by the Department of Social Development) the Federal District, and the State of Mexico agreed on an official definition of the Mexico City Metropolitan Area, and the Valley of Mexico Metropolitan Area on December 22, 2005.[3] Per the agreement, most urban planning projects will be administered by Metropolitan Commissions.
Contents |
Components of the agglomeration
Mexico City Metropolitan Area
The Mexico City Metropolitan Area is defined to be integrated by:
- The 16 boroughs (delegaciones) of the Federal District (Mexico City proper)
|
|
|
|
- The 40 municipalities of the State of Mexico
|
|
|
|
- One conurbation municipality of the State of Hidalgo
- Tizayuca
Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico
The definition of the Mexico City Metropolitan Area is positive, in that all municipalities form a single conurbation. By contrast, the Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico is considered a normative definition, in that it incorporates 18 additional strategic municipalities in the territorial administration of the region, even if they are not fully integrated as of yet. Many urban projects, mostly related to the improvement of air quality and water sanitation, are coordinated for all constituent municipalities of this agglomeration. The majority of the population reports of urban areas in Mexico refer to this agglomeration, and not to the MCMA conurbation.
|
|
|
|
Geography and environment


Greater Mexico City spreads over the valley of Mexico, also called the valley of Anáhuac a 9,560 km² (3,691 sq mi) valley that lies at an average of 2,240 m (7,349 ft) above sea level but below the Tropic of Cancer. Originally, a system of interconnected lakes occupied a large area of the valley, of which Lake Texcoco was the largest. Mexico City was built on the island of Tenochtitlan in the middle of the lake. During conquest of Mexico the dikes that protected the city from recurrent floods were destroyed and colonial authorities preferred to drain the water of the lake, which was, for the most part, shallow. In 1900, president Porfirio Díaz inaugurated the Valley's System of Drainage that hinders the growth of water bodies in the valley (and prevents floods). The basin of the valley of Mexico was thus integrated artificially to the Moctezuma river basin which connects to the River Pánuco. The last remnants of the system of lakes are found in the boroughs of Xochimilco and Tláhuac, and in the municipality of Atenco.
The valley of Mexico is surrounded by mountains on all four sides creating a basin with only one small opening at the north, trapping all exhaust emissions of the city. At the southern part of the basin the mountain range reaches an altitude of 3,952 m (12,965 ft) above sea level; and to the east the volcanoes reach an altitude of more than 5,000 m (16,000 ft). The region receives anti-cyclonic systems, producing weak winds that do not allow for the dispersion of accumulated air pollutants, produced by the 50,000 industries operating in Greater Mexico City and the 4 million vehicles circulating in its roads and highways.[4]
There are several environmental programs in operation in all municipalities of Greater Mexico City. One of them is Hoy No Circula (known in English as "One Day without a Car"), whereby only vehicles with certain ending numbers on their license plates are allowed to circulate on certain days in an attempt to cut down on pollution and traffic congestion. The program groups vehicles by their ending license plate digits, and every weekday vehicles having any of the day's two "hoy no circula" digits are banned from circulating. For instance, on Fridays, vehicles with plates ending in 9 or 0 may not drive. This program is controversial since it has resulted in households buying additional vehicles, whether new cars for better-off houses, or very old cheap—and thus more polluting—vehicles. Moreover newer vehicles are exempt from complying with the program—in that they are manufactured with stricter pollution-reduction equipment—a move said to have been pushed by auto makers to boost sales of new vehicles.
Other environmental programs include the IMECA (Índice Metropolitano de la Calidad del Aire, "Metropolitan Index of Air Quality") a real-time monitoring of the concentrations of several pollutants on the atmosphere of the valley of Mexico. If the IMECA values reach a critical level, an environmental contingency is declared whereby Hoy No Circula is extended to two days per week, industrial activities are reduced, certain gas power plants shut down, and elementary school entry hours are changed. There has been a decrease in the number of environmental contingencies since the 1990s (due to an improvement fuels, the implementation of industrial controls and relocation of factories), from more than 5 to only one or zero a year in the last few years.
Political administration
Like it is the case with all trans-municipal metropolitan areas in Mexico, there is no elected government institution in charge of administering the entire metropolitan area. Each municipality is autonomous to administer its local affairs, regulated by the government of the states they belong to. However, unlike some other large metropolitan areas that are entirely contained in one state, like Greater Guadalajara and Greater Monterrey in which the state government coordinates metropolitan activities, Greater Mexico City spreads over three federal entities—two states and the Federal District—and therefore most of the metropolitan projects have to be agreed upon by government officials of each federal entity and/or overseen by the federal government—since the budget of the Federal District is approved by the Congress of the Union, being the capital of the federation—or through metropolitan commissions.
Economy
From 1940 and until 1980, Greater Mexico City experienced an intense rate of demographic growth concurrent with the economic policy of import substitution. Mexican industrial production was heavily centralized in Greater Mexico City during this period which produced intense immigration to the city. Close to 52% of the economically active population of Greater Mexico City worked in the industry sector in 1970.[5] This situation changed drastically during the period of 1980 to 2000, in which the economic based shifted to the service sector which in 2000 employed close to 70% of the economically active population in the conurbation.[5] The annual rate of growth decreased sharply as well as the regional and national patterns of immigration: residents are moving out of the core city to the suburbs or to nearby cities, whereas the northern states now receive a larger number of immigrants as new hubs of industrial production. Greater Mexico City's main industries are now related to trade, financial services, insurance companies, telecommunications, informatics and transportation.[5] In spite of the recent shifts in economic production and the decentralization of the economic activity promoted by the government, Greater Mexico City's share of total economic activity in the country is still high, though decreasing. Mexico City proper alone produces 21.8% of the nation's Gross Domestic Product.[6]
Demographics
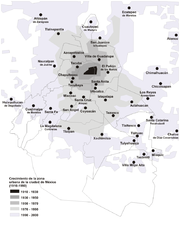
Greater Mexico City is the largest metropolitan area in Mexico and the area with the highest population density. As of 2009, 19,981,801 persons live in this urban agglomeration, of which 8,841,916 live in Mexico City proper.[2] In terms of population, the biggest municipalities that are part of Greater Mexico City (excluding Mexico City proper) are:[2]
- Ecatepec de Morelos (pop. 1,734,701).
- Nezahualcóyotl (pop. 1,086,720).
- Naucalpan (pop. 799,889).
- Tlalnepantla de Baz (pop. 660,953).
- Chimalhuacán (pop. 552,901).
- Ixtapaluca (pop. 535,432).
- Cuautitlán Izcalli (pop. 532,973).
The above municipalities are located in the state of Mexico; in fact, approximately 75% (10 million) of the state of México's population live in municipalities that are part of Greater Mexico City's conurbation.
Greater Mexico City was the fastest growing metropolitan area in the country until the late 1980s. Since then, and through a policy of decentralization in order to reduce the environmental pollutants of the growing conurbation, the annual rate of growth of the agglomeration has decreased, and it is lower than that of the other four largest metropolitan areas (namely Greater Guadalajara, Greater Monterrey, Greater Puebla and Greater Toluca) even though it is still positive.[7] The net migration rate of Mexico City proper from 1995 to 2000, however, was negative,[8] which implies that residents are moving to the suburbs of the metropolitan area, or to other states of Mexico.
Transportation
Greater Mexico City is connected through a private network of toll expressways to the nearby cities of Querétaro, Toluca, Cuernavaca, Pachuca and Puebla. Internally, the Federal District is serviced by arterial roads, locally called ejes viales, while the metro area is connected by two ring roads: the Periférico and Circuito Interior, with an elevated highway running on top of the first one. In 2007 the Eje Troncal Metropolitano will be finished, a highway that will connect Xochimilco with Ciudad Azteca.
The federal government has started the construction of a toll expressway that would connect the expressways of Querétaro and Puebla, so that traffic moving across the country would not have to go into the city. The project is partially completed and local residents of the outermost municipalities use it as a high-speed alternative to travel across the suburbs without having to use the internal arterial roads of the city.
The most important public transportation is the metro, one of the largest in the world with 207 km and 175 stations, that only services Mexico City proper, even though it is further extended by the Xochimilco Light Rail and new lines A and B. A commuter train, the Tren Suburbano, will serve several municipalities of the metropolitan area once it starts operating by mid-2007, with new lines planned.
Unlike other large metropolitan areas, Greater Mexico City is served by only one airport, the Mexico City International Airport or best known as Benito Juárez International Airport, whose traffic exceeds the current capacity. The 2000-2006 federal administrations proposed the construction of a second airport for the metropolitan area to be located at the municipality of Texcoco. Local residents, however, opposed the project, and the government decided to build a second terminal on the restricted area of the current airport, and decentralize flights to the nearby metropolitan areas of Toluca, Puebla, Pachuca and Cuernavaca, which, along with Greater Mexico City, conform a megalopolis (known in Spanish as a corona regional or ciudad-región).[9]
Landmarks

Important landmarks of Greater Mexico City include the Historic Center of Mexico City, the floating gardens of Xochimilco, the Pre-Hispanic city ruins Teotihuacan, located at the municipality of the same name, all three declared World Heritage sites by UNESCO in 1987. The National Parks at the southern portion of the Federal District (over the mountainous range of Ajusco), the Parks of Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl and the National Reserve of Lake Texcoco are some of the environmental landmarks of the valley as well.
See also
- Metropolitan areas of Mexico
- List of metropolitan areas by population
- List of metropolitan areas in the Americas by population
- List of urban agglomerations by population
- List of cities in Mexico
- Demographics of Mexico
References
- ↑ INEGI: Delimitación de las Zonas Metropolitanas de México
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 National Population Council. "Mexico City Metropolitan Area". Government of the State of Mexico. http://www.edomex.gob.mx/poblacion/docs/2009/PDF/ZMVM.pdf. Retrieved 9 December 2009.
- ↑ News article of the agreement to define the metropolitan area
- ↑ Secretaría del Medio Ambiente del Distrito Federal, SMA (2002) Programa para Mejorar la Calidad del Aire de la Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México, Gobierno del Distrito Federal
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Expansión y Reconversión Económica de la Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México, Una Mirada de 1970 a 2000 by Rodolfo Montaño Salazar, UNAM
- ↑ Producto Interno Bruto por entidad federativa, INEGI
- ↑ Síntesis de Resultados del Conteo 2005 INEGI
- ↑ Tasa de emigración, inmigración y migración neta de las entidades federativas
- ↑ Cap 2: Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México PROAIRE, Programa para Mejorar la Calidad del Aire ZMVM 2002-2010
External links
- Escenarios Demográficos y Urbanos de la Zona Metropolitana del Valle de México, published by the Consejo Nacional de Población (CONAPO).
- http://bbs.keyhole.com/ubb/placemarks/cl-11-23-07-406114082.kmz
|
||||||||||